Seed Selection and Seed Treatment (बीज चयन एवं बीज उपचार तकनीकें)
Seed is the most critical input in agriculture. Proper seed selection and seed treatment play a vital role in ensuring healthy crop establishment, higher germination, better resistance to pests and diseases, and increased yield. Using poor-quality or untreated seed can reduce productivity even when other inputs are optimal.
Importance of Seed Selection (बीज चयन का महत्व)
Seed selection determines the genetic potential of the crop. Selecting high-quality seeds ensures:
- Uniform germination and crop growth
- Higher yield potential
- Better tolerance to pests, diseases, and stress
- Efficient use of fertilizers and irrigation
Good seed selection reduces the risk of crop failure and improves overall farm profitability.
Characteristics of Good Quality Seed (अच्छे गुणवत्ता वाले बीज की विशेषताएँ)
A good quality seed should have the following features:
- High germination percentage
- Genetic purity of the variety
- Free from weed seeds and inert matter
- Free from pests and diseases
- Proper moisture content
- Uniform size, shape, and color
Certified or truthfully labeled seeds are preferred as they meet standard quality norms.
Sources of Quality Seeds (गुणवत्तापूर्ण बीज के स्रोत)
Farmers should procure seeds from reliable sources such as:
- Government seed corporations
- Certified seed agencies
- Agricultural universities
- Krishi Vigyan Kendras (KVKs)
- Authorized private seed companies
Using farm-saved seeds should be done only after proper cleaning, grading, and testing.
What is Seed Treatment? (बीज उपचार क्या है?)
Seed treatment is the process of applying physical, chemical, or biological agents to seeds before sowing to protect them from seed-borne and soil-borne diseases, insects, and environmental stress. It also helps improve seed vigor and early crop establishment.
Objectives of Seed Treatment (बीज उपचार के उद्देश्य)
- Protection against seed-borne diseases
- Control of soil-borne pathogens and insects
- Improvement in germination and seedling vigor
- Ensuring uniform crop stand
- Reduction in seed rate and re-sowing cost
Types of Seed Treatment (बीज उपचार के प्रकार)
1. Physical Seed Treatment (भौतिक बीज उपचार)
This method involves non-chemical techniques such as:
- Hot water treatment to control fungal and bacterial diseases
- Sun drying to reduce moisture and pathogen load
- Mechanical cleaning and grading
Physical treatments are eco-friendly but may not provide long-term protection.
2. Chemical Seed Treatment (रासायनिक बीज उपचार)
Chemical treatment involves applying fungicides or insecticides to seeds. Common chemicals include:
- Thiram
- Carbendazim
- Captan
- Imidacloprid
Chemical seed treatment protects seeds during early growth stages and is widely used for cereals, pulses, and oilseeds.
3. Biological Seed Treatment (जैविक बीज उपचार)
Biological treatment uses beneficial microorganisms such as:
- Trichoderma spp.
- Pseudomonas fluorescens
- Rhizobium (for legumes)
This method improves soil health, enhances nutrient availability, and supports sustainable agriculture.
Method of Seed Treatment (बीज उपचार की विधि)
- Measure the recommended quantity of seed.
- Prepare the required dose of treatment chemical or bio-agent.
- Mix seeds uniformly with the treatment material.
- Dry treated seeds in shade before sowing.
- Sow seeds within the recommended time.
Always follow safety precautions while handling chemicals.
Precautions During Seed Treatment (बीज उपचार के दौरान सावधानियाँ)
- Use recommended chemicals and dosages only
- Wear gloves and protective equipment
- Do not mix treated seeds with food or feed
- Avoid direct sunlight after treatment
- Do not wash treated seeds
- Label treated seed bags clearly
Benefits of Seed Treatment (बीज उपचार के लाभ)
- Improved germination and seedling growth
- Reduced disease and pest incidence
- Cost-effective crop protection
- Better crop stand and yield
- Reduced dependency on pesticides later
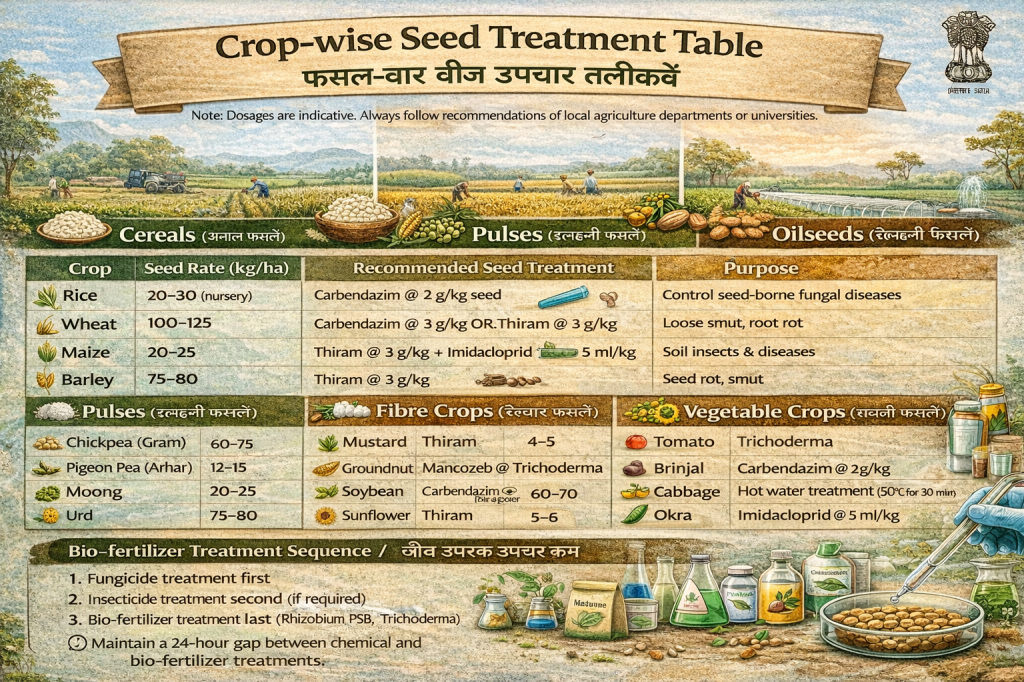
Crop-wise Seed Treatment Table (फसल-वार बीज उपचार तालिका)
Note: Dosages are indicative. Always follow recommendations of local agriculture departments or universities.
Cereals (अनाज फसलें)
| Crop | Seed Rate (kg/ha) | Recommended Seed Treatment | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rice | 20–30 (nursery) | Carbendazim @ 2 g/kg seed | Control seed-borne fungal diseases |
| Wheat | 100–125 | Carbendazim @ 2 g/kg OR Thiram @ 3 g/kg | Loose smut, root rot |
| Maize | 20–25 | Thiram @ 3 g/kg + Imidacloprid @ 5 ml/kg | Soil insects & diseases |
| Barley | 75–80 | Thiram @ 3 g/kg | Seed rot, smut |
Pulses (दलहनी फसलें)
| Crop | Seed Rate (kg/ha) | Recommended Seed Treatment | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chickpea (Gram) | 60–75 | Carbendazim @ 2 g/kg + Rhizobium culture | Wilt control & N fixation |
| Pigeon Pea (Arhar) | 12–15 | Trichoderma @ 5 g/kg + Rhizobium | Disease control & nodulation |
| Moong | 20–25 | Thiram @ 3 g/kg + Rhizobium | Seed rot, better growth |
| Urd | 20–25 | Carbendazim @ 2 g/kg + Rhizobium | Wilt prevention |
Oilseeds (तिलहनी फसलें)
| Crop | Seed Rate (kg/ha) | Recommended Seed Treatment | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mustard | 4–5 | Thiram @ 3 g/kg | Alternaria blight |
| Groundnut | 120–150 | Mancozeb @ 3 g/kg + Trichoderma | Collar rot |
| Soybean | 60–70 | Carbendazim @ 2 g/kg + Bradyrhizobium | Root diseases |
| Sunflower | 5–6 | Thiram @ 3 g/kg | Seed & soil fungi |
Fibre Crops (रेशेदार फसलें)
| Crop | Seed Rate (kg/ha) | Recommended Seed Treatment | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cotton | 2–3 | Imidacloprid @ 5 ml/kg | Sucking pests |
| Jute | 5–7 | Carbendazim @ 2 g/kg | Seedling diseases |
Vegetable Crops (सब्जी फसलें)
| Crop | Seed Rate (kg/ha) | Recommended Seed Treatment | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tomato | 0.4–0.5 | Trichoderma @ 5 g/kg | Damping-off |
| Brinjal | 0.5–0.75 | Carbendazim @ 2 g/kg | Fungal diseases |
| Cabbage | 0.5 | Hot water treatment (50°C for 30 min) | Black rot |
| Okra | 8–10 | Imidacloprid @ 5 ml/kg | Seed-borne pests |
Bio-fertilizer Treatment Sequence (जैव उर्वरक उपचार क्रम)
- Fungicide treatment first
- Insecticide treatment second (if required)
- Bio-fertilizer treatment last (Rhizobium, PSB, Trichoderma)
⏱️ Maintain a 24-hour gap between chemical and bio-fertilizer treatments.
Key Advantages of Crop-wise Seed Treatment
(फसल-वार बीज उपचार के लाभ)
- Better germination and uniform crop stand
- Protection from early-stage pests and diseases
- Reduced cost of plant protection later
- Improved yield and crop health
- Supports sustainable agriculture practices
Role of Seed Selection and Treatment in Sustainable Agriculture (सतत कृषि में बीज चयन एवं उपचार की भूमिका)
Proper seed selection and seed treatment reduce excessive chemical use in the field. Biological seed treatments support eco-friendly farming practices, enhance soil fertility, and improve long-term crop productivity.
Conclusion
Seed selection and seed treatment are simple yet powerful practices that significantly influence crop success. By choosing quality seeds and adopting appropriate seed treatment techniques, farmers can achieve healthy crops, higher yields, and sustainable agricultural growth. These practices form the foundation of modern and scientific farming. Crop-wise seed treatment is a low-cost, high-impact agricultural practice. When done correctly and as per crop requirement, it ensures healthy seedlings, higher productivity, and reduced crop loss, making it an essential step in modern farming.

Leave a comment