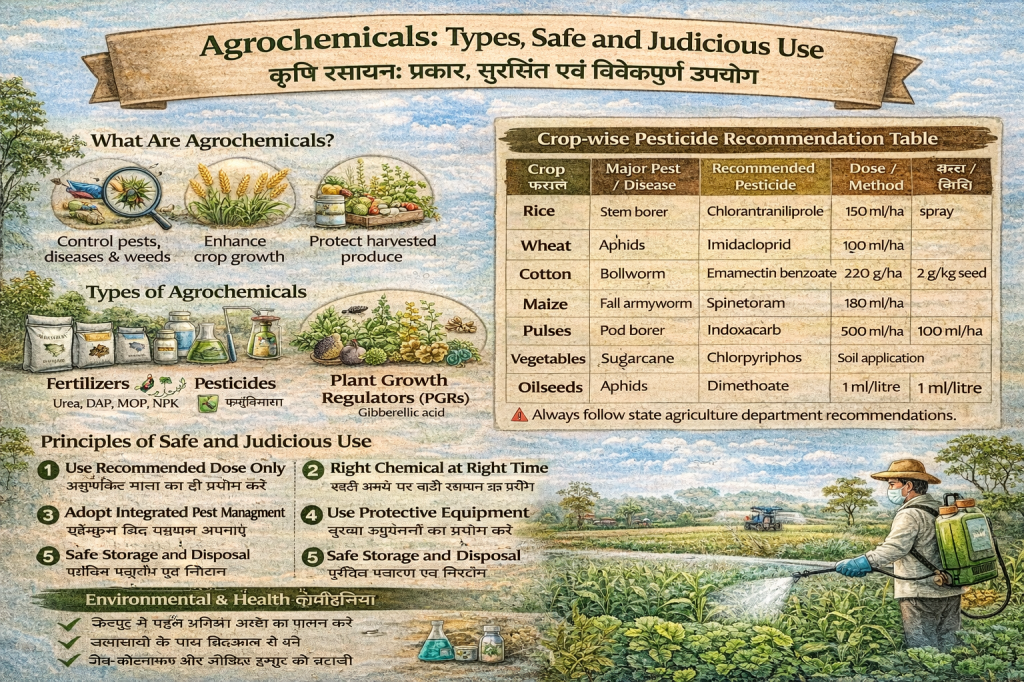
What are Agrochemicals? (कृषि रसायन क्या हैं?)
Agrochemicals are chemical substances used in agriculture to enhance crop growth and protect crops from harmful organisms. These include fertilizers, pesticides, herbicides, fungicides, insecticides, and plant growth regulators.
Agrochemicals play a vital role in modern agriculture by helping farmers increase crop productivity, protect crops from pests and diseases, and manage nutrient deficiencies. When used responsibly, agrochemicals contribute significantly to food security. However, their improper use can harm human health, soil, water, and the environment, making safe and judicious use essential.
They support agriculture by:
- Improving soil fertility
- Controlling pests, diseases, and weeds
- Enhancing crop quality and yield
Classification of Agrochemicals (कृषि रसायनों का वर्गीकरण)
Agrochemicals are broadly classified into the following categories:
1. Fertilizers (उर्वरक)
Fertilizers supply essential nutrients required for plant growth.
Types of Fertilizers
- Nitrogenous fertilizers: Urea, Ammonium sulphate
- Phosphatic fertilizers: DAP, SSP
- Potassic fertilizers: MOP
- Complex fertilizers: NPK
- Micronutrient fertilizers: Zinc sulphate, Boron
Uses
- Improve soil fertility
- Promote vegetative growth and yield
- Correct nutrient deficiencies
2. Pesticides (कीटनाशक)
Pesticides are chemicals used to kill or control pests that damage crops.
Types of Pesticides
- Insecticides: Control insects (e.g., Imidacloprid)
- Fungicides: Control fungal diseases (e.g., Mancozeb)
- Herbicides: Control weeds (e.g., Glyphosate)
- Rodenticides: Control rodents
- Nematicides: Control nematodes
3. Insecticides (कीट नियंत्रण रसायन)
Used to manage insect pests that affect crops at different stages.
Common Groups
- Organophosphates
- Carbamates
- Synthetic pyrethroids
- Neonicotinoids
Methods of Use
- Seed treatment
- Foliar spray
- Soil application
4. Fungicides (फफूंदनाशक)
Fungicides prevent and control fungal diseases like rust, blight, and wilt.
Types
- Contact fungicides (e.g., Copper oxychloride)
- Systemic fungicides (e.g., Carbendazim)
5. Herbicides (खरपतवारनाशक)
Herbicides control unwanted plants (weeds) that compete with crops.
Types
- Pre-emergence herbicides: Applied before weed emergence
- Post-emergence herbicides: Applied after weed emergence
6. Plant Growth Regulators (PGRs) (पादप वृद्धि नियामक)
PGRs modify plant growth processes.
Examples
- Auxins
- Gibberellins
- Cytokinins
Uses
- Improve flowering and fruit setting
- Control plant height
- Increase yield quality
Methods of Agrochemical Application (कृषि रसायनों के प्रयोग की विधियाँ)
- Seed treatment: Protects seeds and seedlings
- Soil application: Applied directly to soil
- Foliar spray: Sprayed on leaves
- Drip/fertigation: Through irrigation system
- Dusting: Used mainly for insect control
Correct method selection ensures maximum effectiveness and minimum loss.
Use of Agrochemicals (कृषि रसायनों का सुरक्षित एवं विवेकपूर्ण उपयोग)
The safe and judicious use of agrochemicals is critical to protect farmers, consumers, and the environment.
Principles of Judicious Use
- Use agrochemicals only when necessary
- Follow recommended dose and timing
- Choose crop-specific and pest-specific chemicals
- Prefer integrated pest management (IPM)
Safety Measures During Use (प्रयोग के दौरान सुरक्षा उपाय)
- Wear protective clothing, gloves, and masks
- Avoid eating, drinking, or smoking during spraying
- Spray in calm weather conditions
- Avoid overuse and repeated use of the same chemical
- Follow waiting period before harvest
Environmental and Health Concerns (पर्यावरण एवं स्वास्थ्य संबंधी चिंताएँ)
Improper use of agrochemicals can lead to:
- Soil and water pollution
- Pesticide residues in food
- Development of pest resistance
- Health hazards to humans and animals
Hence, responsible usage is essential.
Role of IPM and INM in Reducing Chemical Use (IPM एवं INM की भूमिका)
- Integrated Pest Management (IPM): Combines biological, cultural, and chemical control
- Integrated Nutrient Management (INM): Balances chemical and organic fertilizers
These approaches reduce chemical dependency and promote sustainable farming.
Advantages of Proper Agrochemical Use (उचित कृषि रसायन उपयोग के लाभ)
- Increased crop yield and quality
- Reduced crop losses
- Cost-effective farming
- Environmental protection
- Food safety
Conclusion
Agrochemicals are powerful tools in modern agriculture, but their benefits can only be realized through safe, scientific, and judicious use. Farmers must follow recommended practices, adopt IPM principles, and remain aware of environmental and health impacts. Responsible agrochemical management ensures sustainable agriculture, food security, and farmer well-being.

Leave a comment