What is Integrated Scheme for Agricultural Marketing (ISAM)?
The Integrated Scheme for Agricultural Marketing (ISAM) is a Government of India initiative under the Ministry of Agriculture & Farmers’ Welfare aimed at strengthening agricultural marketing systems to ensure better price realization for farmers, reduce post-harvest losses, and promote efficient, transparent, and competitive markets.
ISAM integrates several sub-schemes to address infrastructure gaps, market reforms, information dissemination, and farmer participation in agricultural marketing.
Objectives of ISAM
- Improve market access for farmers
- Reduce intermediaries and transaction costs
- Promote scientific storage and grading
- Encourage transparent price discovery
- Strengthen market intelligence and digital platforms
- Support value addition and rural agri-economy
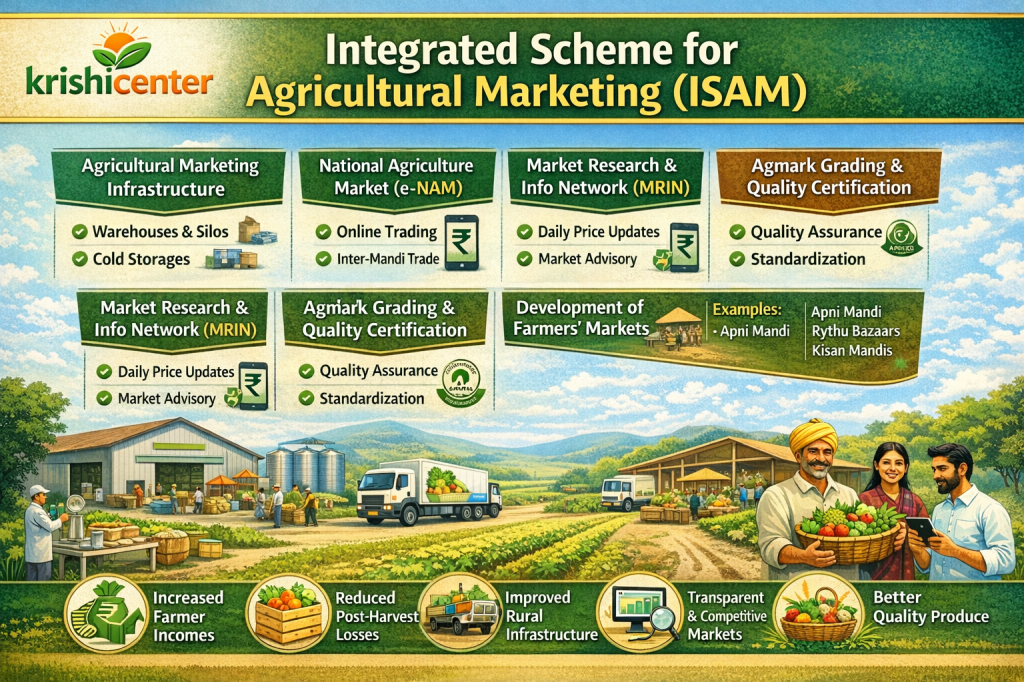
Major Components of ISAM
1. Agricultural Marketing Infrastructure (AMI)
Earlier known as GrAMIN Bhandaran Yojana
Purpose
- Create and upgrade scientific storage infrastructure
- Prevent distress sale by farmers
- Promote warehouse receipt financing
Key Features
- Construction of warehouses, silos, godowns
- Cold storage units and pack houses
- Facilities for grading, sorting, and standardization
Benefits
- Reduced post-harvest losses
- Improved quality of produce
- Access to bank credit against warehouse receipts
2. National Agriculture Market (e-NAM)
A pan-India electronic trading portal
Purpose
- Integrate existing APMC mandis into a single national market
- Enable transparent and competitive trading
Key Features
- Online bidding and e-auction
- Real-time price discovery
- Quality assaying and electronic weighment
- Inter-state and inter-mandi trade
Impact
- Reduces information asymmetry
- Encourages better price realization
- Enhances farmer bargaining power
3. Market Research and Information Network (MRIN)
Purpose
- Provide timely and accurate market information
Key Features
- Daily price and arrival data from mandis
- Market trends and advisory services
- Dissemination via websites, mobile apps, SMS, and media
Importance
- Helps farmers decide when and where to sell
- Reduces price exploitation
4. Strengthening of Agmark Grading Facilities
Purpose
- Promote quality assurance and standardization
Key Features
- Upgradation of Agmark laboratories
- Training of personnel in grading and certification
- Awareness programs on quality standards
Benefits
- Improves consumer confidence
- Facilitates domestic and export trade
- Encourages premium pricing for quality produce
5. Development of Farmers’ Markets
Purpose
- Promote direct marketing from farmers to consumers
Examples
- Apni Mandi
- Rythu Bazaars
- Kisan Mandis
Benefits
- Higher farmer share in consumer price
- Fresh produce at lower prices for consumers
- Reduced role of middlemen
Funding Pattern
- Central Government provides financial assistance
- State Governments, Panchayats, FPOs, cooperatives, and private entities are eligible
- Subsidy varies based on region, category, and infrastructure type
Role of States
- Reform APMC Acts to allow:
- Direct marketing
- E-trading
- Single-point levy of market fees
- Facilitate land, approvals, and implementation support
Benefits of ISAM
- 📈 Increased farmer income
- 📉 Reduced post-harvest losses
- 🏗️ Improved rural infrastructure
- 🔍 Transparent and competitive markets
- 🌾 Better quality produce and food security
Challenges
- Uneven adoption of market reforms across states
- Limited digital literacy among small farmers
- Infrastructure gaps in remote areas
- Need for stronger private sector participation
Conclusion
The Integrated Scheme for Agricultural Marketing plays a crucial role in transforming India’s agricultural marketing. It changes from a fragmented, local system to a national, technology-driven market ecosystem. ISAM combines infrastructure development, digital platforms, quality assurance, and farmer-centric reforms. This combination supports the vision of Doubling Farmers’ Income. It also promotes sustainable agricultural growth.

Leave a reply to Agricultural Marketing Infrastructure – KrishiCenter Cancel reply